Replacing Brick Facade on House A Comprehensive Guide
Replacing a brick facade on a house is a significant undertaking, often transforming a home’s exterior. This guide delves into every aspect of the process, from initial planning and cost analysis to the final installation and post-project considerations.
We’ll explore various brick types, design options, and potential material choices. Detailed cost breakdowns, including labor and hidden costs, will help you budget effectively. Plus, we’ll cover crucial steps like obtaining permits, installation methods, and essential post-installation maintenance.
Introduction to Brick Facade Replacement: Replacing the Brick Facade On a House

Replacing a brick facade is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning, execution, and consideration of various factors. This process can enhance the aesthetic appeal of a home, improve its structural integrity, and often increase its market value. Understanding the different types of brick, the process itself, and the motivations behind such a project is crucial for homeowners contemplating this renovation.
The process involves careful removal of the existing brick, often coupled with addressing any underlying structural issues. New bricks, or a different brick material, are then installed, adhering to specific building codes and architectural guidelines. This detailed approach ensures both a beautiful and durable final result.
Types of Brick Facades
Brick facades come in diverse varieties, each offering unique characteristics and aesthetics. Different types of bricks are manufactured using various techniques and materials, resulting in distinct textures, colors, and patterns. These distinctions are crucial in achieving the desired visual effect and matching the architectural style of the home.
- Common Brick: A traditional choice, common brick is readily available in various colors and sizes. Its durability and relatively low cost make it a popular option for homeowners.
- Facing Brick: Used primarily for its aesthetic appeal, facing brick often boasts a more decorative appearance compared to common brick. It is frequently selected for its visual appeal and texture, though it might come at a higher price point.
- Handmade Brick: Handmade brick exhibits a distinctive, slightly irregular texture, lending a rustic or traditional feel. This unique characteristic is often sought for its visual charm and historical associations.
Reasons for Choosing Facade Replacement: Replacing the brick facade on a house
Homeowners undertake brick facade replacements for a variety of reasons, including aesthetic enhancement, addressing structural issues, and increasing property value.
- Aesthetic Improvement: Replacing a faded or damaged brick facade can dramatically improve a home’s curb appeal. This is a significant factor for many homeowners, as a visually appealing exterior can increase property value and create a more welcoming atmosphere.
- Structural Repair: Brick facades can suffer from deterioration over time, leading to cracks, gaps, or structural instability. Replacing the facade can correct these issues, improving the long-term integrity of the house.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: A new brick facade can improve insulation and reduce energy loss, leading to lower utility bills. This aspect is becoming increasingly important in today’s climate-conscious society.
Planning a Brick Facade Replacement Project
A well-planned project is essential for a successful brick facade replacement. The planning stage involves careful consideration of various factors, from budget allocation to architectural design.
- Assessment and Design: Thorough assessment of the existing facade is critical. This includes identifying any structural issues, determining the desired aesthetic, and planning for the new facade’s design. Consultations with architects or contractors are often necessary for a comprehensive assessment and design phase.
- Budgeting and Material Selection: A detailed budget is essential to manage costs effectively. Careful consideration of different brick types, materials, and installation methods is critical to ensure the project stays within budget constraints.
- Permitting and Regulations: Obtaining the necessary permits and adhering to local building codes is crucial. This step ensures compliance with regulations and avoids potential legal issues.
- Contractor Selection: Choosing a reputable and experienced contractor is vital for a successful project. Research and interviewing potential contractors are essential steps in this process.
Cost Analysis and Budgeting
A crucial aspect of any facade replacement project is a meticulous cost analysis and budget. Understanding the potential expenses, both direct and indirect, is vital for making informed decisions and avoiding costly surprises. This section delves into the intricacies of estimating costs, identifying hidden expenses, and developing a robust budget that incorporates contingencies.
Material Cost Comparison
Different materials significantly impact the overall cost of a brick facade replacement. The cost of the chosen material, including labor and installation, needs careful consideration. Factors like availability, durability, and aesthetic appeal influence the final price.
| Material | Estimated Cost (per square foot) | Labor Cost (per square foot) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Clay Brick | $10 – $20 | $5 – $10 | Traditional choice, but varying quality affects price. |
| Reclaimed Brick | $15 – $30 | $6 – $12 | Higher cost due to sourcing and potential restoration work. |
| Stone Veneer | $25 – $50 | $8 – $15 | Aesthetically pleasing, but requires specialized installation. |
| Composite Materials | $15 – $35 | $6 – $12 | Modern alternatives with varying properties and costs. |
Hidden Costs
Beyond the visible materials and labor, several hidden costs can significantly impact the project’s overall budget. These can include unforeseen issues during demolition, adjustments for structural issues, permits and inspections, and additional materials required due to site conditions. Thorough site assessments and inspections are vital to minimize such surprises.
Budget Creation and Contingencies
A comprehensive budget for a brick facade replacement should encompass all anticipated expenses. This includes detailed estimates for materials, labor, permits, inspections, and any potential unforeseen circumstances.
A well-defined contingency fund, allocated for unexpected issues, is crucial. This fund should be a percentage of the total estimated cost.
A common contingency amount is 10-15% of the total project cost. This buffer addresses unexpected discoveries, material price fluctuations, and potential delays.
Savings and Cost-Effective Solutions
Implementing cost-effective strategies can significantly reduce the project’s overall expense. Exploring options like purchasing materials in bulk, choosing cost-effective but durable materials, and employing experienced contractors with competitive rates can optimize the project’s budget.
- Material Sourcing: Exploring local suppliers and distributors can sometimes reduce transportation costs, potentially leading to savings.
- Phased Implementation: If possible, breaking down the project into smaller phases can allow for more controlled spending and reduce the overall financial strain.
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Integrating energy-efficient elements during the replacement, such as improved insulation, can yield long-term savings on utility bills.
Materials and Design Considerations

Source: bigstockphoto.com
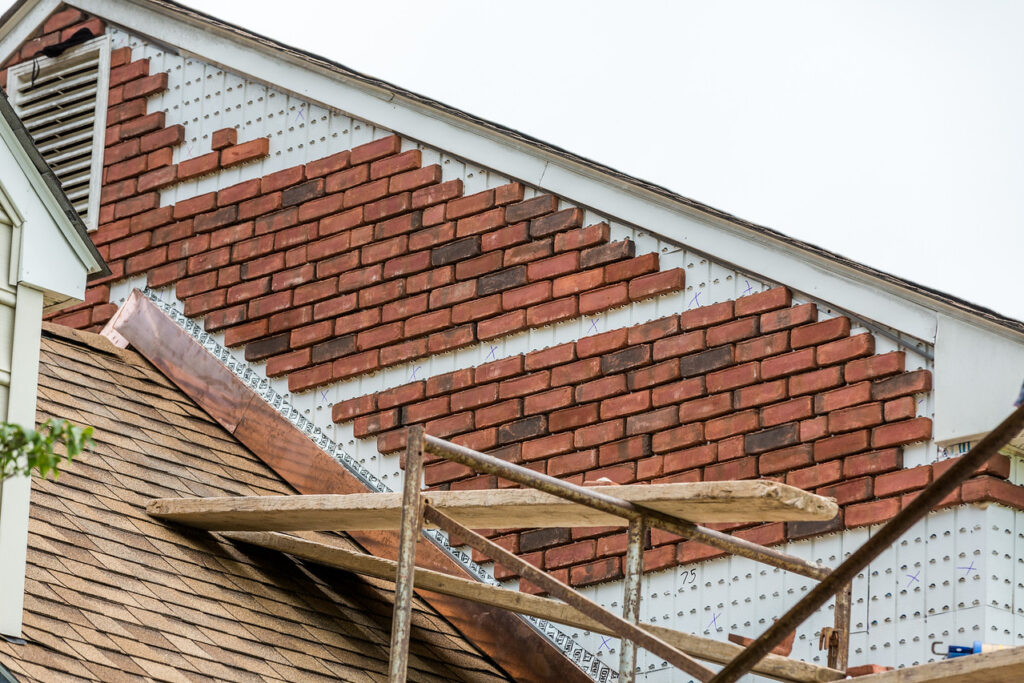
Choosing the right materials and design for a brick facade replacement is crucial for both the longevity and aesthetic appeal of your home. Careful consideration of brick types, color palettes, and patterns will significantly impact the project’s success. Understanding the interplay between materials and architectural style is vital to achieving a harmonious and enduring result.
Careful evaluation of various brick types, design options, and environmental factors will guide the decision-making process. This ensures that the new facade not only enhances the visual appeal but also meets long-term durability standards and respects environmental concerns.
Brick Type Durability and Maintenance
Different brick types exhibit varying levels of durability and maintenance needs. Clay bricks, a traditional choice, are known for their strength and resistance to weathering. However, they may require more frequent cleaning and sealing compared to some more modern options. Concrete bricks offer a cost-effective alternative, but their durability can be influenced by the specific mix and curing process. Manufactured bricks, often made from fired clay or concrete, provide a balance between cost and performance. Their durability depends heavily on the manufacturing process and quality control. Understanding the specific properties of each brick type is essential for selecting the best option for your needs.
Design Options for the New Brick Facade
The design of the new brick facade presents a multitude of possibilities. Color palettes can dramatically alter the house’s appearance. A warm, earthy palette might evoke a rustic charm, while a cool, modern palette could create a contemporary look. Patterns, such as running bond, herringbone, or basket weave, can add visual interest and depth to the facade. The texture of the brick, whether smooth, rough, or textured, further contributes to the overall aesthetic. Consideration of the existing architectural style is paramount to ensure a cohesive and visually appealing result.
Impact on Architectural Style
The new brick facade’s design should complement the existing architectural style of the house. For example, a Victorian home might benefit from a brick facade with intricate patterns and a rich color palette, while a modern home might be enhanced by a minimalist approach with a sleek, smooth texture. A careful study of the house’s history and original design elements will provide crucial insight into the most suitable aesthetic choices.
Comparison of Facade Materials
| Material | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Clay Brick | High durability, excellent weathering resistance, and traditional aesthetic | Higher maintenance (cleaning, sealing), potentially more expensive |
| Concrete Brick | Cost-effective, relatively durable | Durability can vary based on mix and curing, potentially less aesthetic appeal. |
| Manufactured Brick | Balance of cost and performance, diverse design options | Durability depends on manufacturing quality, potential variations in appearance |
This table highlights the key characteristics of different facade materials. Careful consideration of these pros and cons will assist in selecting the optimal material for your project.
Environmental Concerns
Environmental concerns related to facade materials should be considered. The production of certain bricks can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing locally sourced or recycled materials can minimize this impact. Consider the long-term sustainability of the material and its lifecycle impact when making your selection. The embodied energy of a material, which refers to the total energy used in its production, transportation, and installation, is also a critical factor in the environmental assessment.
Planning and Permits

A successful brick facade replacement project hinges on meticulous planning and adherence to local regulations. Properly navigating the permitting process ensures the project aligns with building codes and local ordinances, avoiding potential delays and legal issues. This section articulates the critical steps involved in securing necessary permits and approvals.
Obtaining the necessary permits and approvals is paramount for a brick facade replacement project. Failure to comply with regulations can lead to project delays, significant fines, or even project stoppage. A thorough understanding of local codes and regulations is essential.
Importance of Permits and Approvals
Obtaining necessary permits and approvals is crucial to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations. This protects the homeowner from legal ramifications and guarantees the project meets safety standards. Non-compliance can lead to substantial penalties, project delays, or even a complete halt to the project.
Steps in the Permitting Process
The permitting process typically involves several stages. A crucial first step is researching local building codes and regulations. The specific requirements can vary significantly by municipality or county. This initial research establishes a solid foundation for the project. Detailed plans and specifications should be submitted with the application. The submission should include architectural drawings, material specifications, and project timelines. The application should also clearly articulate the scope of work and any relevant historical context of the existing structure. The next step involves applying to the relevant permitting authority. The application should be accompanied by all required documents. A detailed timeline and schedule for inspections should be agreed upon and documented. The permitting authority will review the application and supporting documentation to ensure compliance with local codes. If additional information is needed, the applicant will be notified. After the review process, if the application is approved, the project can move forward.
Regulations and Codes
Building codes and regulations vary by location. For instance, historic districts often have stricter guidelines for facade replacements, emphasizing the preservation of architectural character. Modern building codes emphasize energy efficiency and safety standards. It’s essential to consult with local authorities to understand specific regulations and obtain a comprehensive understanding of any potential restrictions. Understanding the unique local regulations is vital to ensure the project adheres to all relevant standards and avoids potential problems.
Project Plan Stages
A well-defined project plan is essential for a smooth and timely project. The project plan should include detailed timelines and deadlines for each stage, such as material procurement, design revisions, and construction activities. A comprehensive schedule will be developed to manage the project effectively. A realistic timeline is essential to manage expectations and avoid delays. The plan should incorporate contingency plans for potential delays or unforeseen circumstances.
Inspection Procedures
Inspections are critical throughout the project. Pre-construction inspections are vital for ensuring that the foundation is in good condition and that the construction plans are consistent with local building codes. Inspections during construction ensure that the work is performed according to the approved plans and building codes. These inspections are essential for safety and quality control. Post-construction inspections confirm that the work meets all requirements. A clear understanding of inspection procedures is crucial for project success. A well-defined schedule for these inspections should be included in the project plan.
Installation and Construction
Installing a new brick facade is a complex process requiring careful planning and execution. The method chosen significantly impacts the project’s timeline, cost, and the final aesthetic result. Thorough consideration of various installation techniques, along with the involvement of skilled professionals, is crucial for a successful outcome.
Methods of Brick Facade Installation
Several methods exist for installing a new brick facade, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. These techniques vary in complexity, cost, and the final appearance of the facade. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions.
Comparison of Installation Techniques
The following table provides a comparison of common brick facade installation techniques, highlighting their key features.
| Installation Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mortar-Based Installation | Traditional and proven method; allows for customization of brick patterns and joints; relatively straightforward for skilled installers. | Can be labor-intensive; susceptible to weather damage if not properly sealed; potential for unevenness if not meticulously executed. |
| Dry-Stack Installation | Faster installation time compared to mortar-based; creates a clean, modern aesthetic; reduces potential for water damage. | Requires specialized materials and skilled installers; less flexible in terms of brick patterns; may not be suitable for all types of buildings. |
| Brick Veneer Installation | Allows for the use of various brick types and colors; relatively easier to install than a full brick replacement; cost-effective option. | May not offer the same structural integrity as a full brick replacement; less durable than other techniques; potentially less visually appealing for some projects. |
Step-by-Step Installation Guide (Mortar-Based)
This guide articulates the general steps involved in installing a new brick facade using a mortar-based method. This method requires a skilled team of bricklayers and specialized equipment.
- Preparation: Thoroughly clean and prepare the existing wall surface. Remove any loose or damaged materials, ensuring a level base for the new brickwork. Proper surface preparation is vital for a long-lasting installation.
- Scaffolding Setup: Securely install scaffolding to provide a safe and stable working platform for the installers. The scaffolding must be robust enough to handle the weight of materials and installers.
- Laying the Foundation: Establish a strong foundation by laying a layer of mortar. Ensuring proper levels and alignment is essential for a straight and aesthetically pleasing facade.
- Brick Placement: Carefully place the bricks in the designated spots, ensuring proper spacing and alignment with the previously laid bricks. This step requires precise placement to achieve a uniform appearance.
- Mortar Application: Apply mortar between the bricks, ensuring a consistent and even layer. The mortar should be mixed and applied according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Grouting and Finishing: After the mortar has set, grout the joints to fill any gaps. Finally, clean any excess mortar and grout from the facade.
- Inspection and Quality Control: Conduct thorough inspections to ensure the work meets the required standards. This involves checking for any gaps, unevenness, or other imperfections.
Importance of Scaffolding and Safety
Scaffolding is not just a convenience; it’s a crucial safety element during brick facade installation. Falls from heights are a significant risk in construction, and proper scaffolding mitigates this risk. Safety harnesses, helmets, and other protective gear should be worn at all times.
Role of Professionals
A successful brick facade replacement project relies on the expertise of several professionals. These include:
- General Contractor: Oversees the entire project, ensuring coordination between subcontractors and adherence to the project plan.
- Bricklayer: Skilled in laying bricks, ensuring precise placement and proper mortar application.
- Mason: Experienced in working with stone and brick, often involved in complex installations.
- Architect or Designer: Provides technical guidance and ensures the facade design aligns with building codes and aesthetic goals.
- Safety Officer: Ensures adherence to safety regulations and protocols throughout the installation process.
Post-Installation Considerations
A newly installed brick facade represents a significant investment in your home’s aesthetic and structural integrity. Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure its longevity and preserve its beauty. Neglecting upkeep can lead to costly repairs and premature deterioration. This section includes Artikels’ essential post-installation considerations for maintaining a beautiful and durable brick facade.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Maintaining a brick facade is not just about aesthetics; it’s a proactive measure to prevent costly damage and extend the lifespan of your investment. Regular upkeep protects the brick from environmental stressors like rain, sun, and temperature fluctuations. These elements can cause deterioration, cracking, or discoloration over time. Consistent maintenance ensures the integrity of the mortar, which binds the bricks together and prevents water penetration, a common culprit in brick facade degradation.
Maintenance Tips and Recommendations
Regular cleaning and upkeep are vital for preserving the appearance and durability of a brick facade. This includes:
- Cleaning: Use mild detergent and water to clean the facade regularly. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners that can damage the brick or mortar. Consider using a soft-bristled brush or a garden hose with a gentle spray to remove dirt and debris. Professionals may use specialized cleaning equipment for large-scale projects.
- Protecting from moisture: Address any water penetration issues immediately. This may involve fixing leaky gutters, downspouts, or addressing issues with the roof or foundation. A properly functioning drainage system is critical.
- Inspecting for damage: Regular visual inspections are essential. Look for cracks, loose bricks, or deteriorated mortar. Small issues caught early can be repaired before they escalate into major problems. Use binoculars or a ladder for hard-to-reach areas.
- Addressing efflorescence: Efflorescence is a white or salt-like deposit that forms on the surface of bricks. This occurs when soluble salts in the brick or mortar are dissolved and deposited by water. Addressing the source of moisture is critical in preventing its recurrence.
- Preventing moss and algae growth: Regular cleaning and prompt addressing of moisture issues help prevent moss and algae from growing on the brick surface. These can discolor and damage the facade.
Need for Regular Inspections and Repairs
Regular inspections and timely repairs are critical for preventing costly damage and extending the life of the brick facade. Minor issues, if ignored, can escalate into significant structural problems. An annual or biannual inspection by a qualified professional can detect potential problems early on.
Addressing Potential Issues After Installation
Potential issues may arise after installation, including:
- Cracks or damage: Cracks or damage to the bricks or mortar can occur due to settling, stress, or freeze-thaw cycles. Prompt repairs are vital to prevent further damage and maintain structural integrity. Example: A crack in the mortar line of a facade could indicate underlying structural issues.
- Water penetration: Water penetration can cause damage to the bricks, mortar, and underlying structures. Early detection and repair are crucial to prevent moisture-related problems like mold, mildew, and structural weakening. Example: Water stains or discoloration around the base of the facade may indicate a water infiltration problem.
- Pest infestation: Termites or other pests can damage the wood framing or supporting structures beneath the brick. Regular inspections for signs of infestation are crucial to preventing extensive damage.
Warranties and Guarantees
Warranties and guarantees related to the new brick facade vary depending on the materials, installation, and contractor. Review the warranty documents carefully and note any limitations or conditions. Contact the contractor or manufacturer for clarification on any issues.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world brick facade replacement projects offer valuable insights into the process, costs, and outcomes. Analyzing successful projects provides a practical understanding of the factors that influence the success of such endeavors. This section will showcase diverse examples, highlighting different styles, materials, and the impact on property values.
Successful Project Examples
Several projects demonstrate the successful implementation of brick facade replacements. The key to a successful project often lies in careful planning, precise execution, and a clear understanding of the potential challenges.
- Project A: This project involved a Victorian-era home, showcasing the revitalization of a historically significant facade. Using reclaimed brick, the project successfully preserved the original aesthetic while addressing modern maintenance concerns. This demonstrates how historical preservation and modern improvements can be combined in a brick facade replacement. The project cost approximately $50,000, with the time frame lasting 8 weeks, and the project was completed without major complications.
- Project B: A contemporary home underwent a complete brick facade replacement using a modern, light-gray brick. This transformation improved the curb appeal and updated the home’s exterior design. The cost was approximately $75,000, with the project taking 10 weeks. The project involved significant coordination with local building inspectors due to the project’s proximity to historical landmarks.
- Project C: A project on a mid-century modern house involved replacing the existing brick with a more textured, reddish-brown brick. This updated the house’s design without losing its original charm. The estimated cost was $60,000, and the project took 12 weeks to complete. This project involved significant time in coordinating the delivery of specialized materials.
Summary Table of Project Elements
The following table summarizes key aspects of the selected projects.
| Project | Cost (USD) | Time (weeks) | Materials | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project A | 50,000 | 8 | Reclaimed brick, mortar | None |
| Project B | 75,000 | 10 | Light-gray brick, mortar | Coordination with inspectors |
| Project C | 60,000 | 12 | Reddish-brown textured brick, mortar | Material delivery coordination |
Design Options for Brick Facades
Different design options are available for brick facades. The choice of design depends on the architectural style of the home and the desired aesthetic.
- Image 1: A classic brick facade with a traditional, straight-line pattern. The bricks are a warm, reddish-brown color, and the mortar is a matching shade. This style evokes a sense of timeless elegance and is often suitable for older homes.
- Image 2: A modern brick facade with a more complex, layered pattern. The bricks are a neutral gray color, and the mortar is a contrasting light gray. This style is more contemporary and can add a touch of sophistication to a modern home.
- Image 3: A brick facade with a combination of different brick types. The facade features a mix of sizes and colors, creating a visually interesting and dynamic effect. This style is suitable for homes that want a unique and distinctive aesthetic.
Impact on Property Value
Brick facade replacements can significantly enhance property value. Studies have shown that well-executed projects can increase property values by 5-15%, depending on the market and location. This increase is attributed to improved curb appeal, increased structural integrity, and enhanced aesthetic appeal.
Homeowner Feedback
Homeowners generally report positive feedback regarding their brick facade replacements. Many express satisfaction with the improved appearance, increased property value, and the updated curb appeal. Occasionally, some homeowners might experience minor issues with the installation process or material delivery, but these issues are generally resolved quickly and professionally.
Closure
In conclusion, replacing a brick facade on a house is a multifaceted project requiring careful planning, budgeting, and execution. By understanding the various steps, material options, and potential challenges, homeowners can embark on this renovation with confidence. Ultimately, the results can significantly enhance the property’s value and aesthetic appeal. The key takeaway is to approach this project thoughtfully, considering all factors to achieve the desired outcome.





