Facade Design Services A Comprehensive Guide
Facade design services are crucial for creating visually appealing and functional buildings. This guide explores the intricacies of facade design, encompassing everything from material selection to energy efficiency considerations and the crucial role of skilled professionals. We’ll delve into the various styles, materials, and services offered, ultimately empowering you to make informed decisions for your next project.
Different facade design styles, from modern minimalism to traditional aesthetics, each offer unique advantages and challenges. Understanding these nuances is essential to achieving a building that resonates with its surroundings and serves its intended purpose. We’ll also examine how facade design integrates seamlessly with a building’s structural and mechanical systems, creating a harmonious whole.
Facade Design Considerations
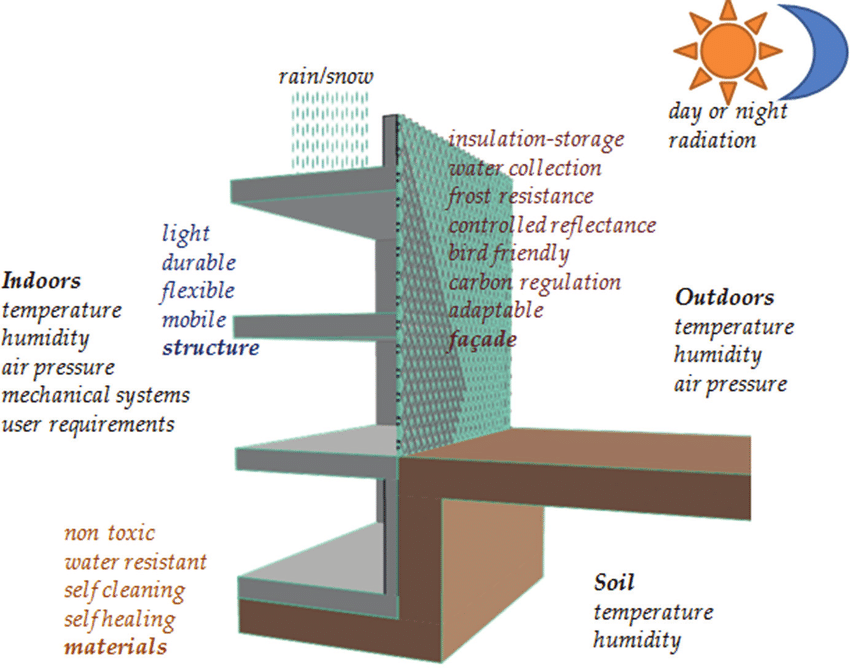
Facade design is a critical aspect of building architecture, influencing not only the aesthetic appeal but also the building’s performance and sustainability. Careful consideration of design styles, materials, and energy efficiency strategies is paramount to creating a structure that is both visually appealing and functionally sound. The facade is the first impression of a building and speaks volumes about its design philosophy.
Effective facade design considers a multitude of factors, including the surrounding environment, local building codes, and the intended use of the structure. A well-designed facade can enhance natural light penetration, improve thermal comfort, and reduce energy consumption. By carefully selecting materials and incorporating sustainable design principles, architects can create facades that are both beautiful and environmentally responsible.
Facade Design Styles
Different facade design styles evoke distinct aesthetic impressions and functional attributes. Modern styles often feature clean lines, minimalist forms, and large expanses of glass, emphasizing functionality and contemporary aesthetics. Traditional styles, on the other hand, often incorporate historical elements, ornamentation, and natural materials, reflecting a connection to the past. Sustainable styles prioritize environmentally conscious design, incorporating materials with low embodied energy, high recyclability, and energy-efficient features. Each style offers unique advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, maintenance, and visual impact.
Facade Materials and Their Properties, Facade design services
Facade materials play a crucial role in the overall performance and appearance of a building. The choice of material significantly affects the building’s energy efficiency, durability, and aesthetic qualities. Common facade materials include glass, brick, metal, and composite materials.
- Glass facades offer excellent natural light transmission, contributing to a bright and airy interior. However, they can be susceptible to heat gain in warm climates and require specialized treatments to control solar heat. Examples include curtain wall systems and large glazed openings, which have been used in modern architectural marvels like the Burj Khalifa.
- Brick facades provide a classic and durable aesthetic, with excellent thermal mass properties. They offer a strong sense of permanence and historical character. Brick can be a cost-effective material, but its installation can be labor-intensive and may not be as adaptable to modern design aesthetics as other materials.
- Metal facades are versatile and can be shaped into various forms, offering a modern and sleek appearance. Aluminum and steel are common choices, often used in combination with glass. Metals can be susceptible to corrosion and require regular maintenance. Stainless steel, however, is highly resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for demanding environments.
Energy Efficiency in Facade Design
Energy efficiency is paramount in modern facade design. Energy-efficient facades reduce the building’s reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Strategies for achieving energy efficiency in facade design include:
- Using insulation materials such as expanded polystyrene or polyurethane to minimize heat transfer through the facade. High-performance insulation helps reduce the need for energy-intensive heating and cooling systems.
- Employing shading devices, such as overhangs or external sunscreens, to reduce solar heat gain in warm climates. Strategic shading can effectively minimize heat buildup in the building.
- Optimizing window placement and glazing type to maximize natural light while minimizing heat transfer. The orientation of windows and the type of glass used can significantly impact energy consumption.
Impact on Building Aesthetics and Architectural Expression
Facade design significantly impacts the overall architectural expression of a building. A well-designed facade can enhance the building’s visual appeal and communicate its function and purpose. The choice of materials, colors, and patterns can contribute to the building’s unique character and identity.
Thermal Performance of Facade Materials
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Solar Heat Gain Coefficient | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass (Double-pane, Low-E) | 0.8-1.2 | 0.4-0.6 | Excellent light transmission, moderate thermal performance |
| Brick (Standard) | 0.7-1.0 | 0.5-0.7 | High thermal mass, good insulation, traditional aesthetic |
| Metal (Aluminum) | 150-200 | 0.1-0.3 | Excellent reflectivity, potentially high thermal performance with appropriate insulation |
Services Offered by Facade Design Professionals
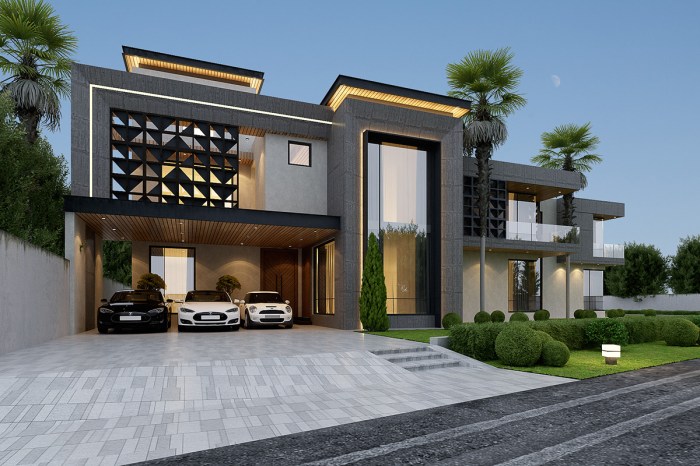

Source: behance.net
Facade design professionals play a crucial role in the success of any building project. Their expertise extends beyond aesthetics, encompassing technical considerations and ensuring the long-term performance of the facade. This expertise is vital for creating functional, durable, and visually appealing exterior spaces.
Facade design firms provide a comprehensive range of services tailored to meet the unique needs of each project. These services are carefully coordinated to optimize design, construction, and the overall building performance.
Types of Services
Facade design services encompass a spectrum of activities, from initial conceptualization to final construction. The diverse range of services offered by these professionals ensures a seamless and well-executed project.
- Concept Design: This initial phase involves developing the overall design vision for the facade. This includes exploring various aesthetic options, material choices, and structural configurations to create a compelling and functional design that aligns with the building’s intended purpose and architectural style. It also considers factors such as daylighting, energy efficiency, and accessibility.
- Detailed Design: This stage refines the concept design, specifying precise details for construction. This includes technical drawings, material specifications, and fabrication details, ensuring clarity and accuracy for the fabrication and installation process. This crucial step guarantees that the design translates effectively into a real-world structure.
- Construction Administration: This service ensures that the facade design is executed according to the approved plans and specifications. It involves managing the construction process, coordinating with contractors, inspecting work, and resolving any design or construction issues that arise during the project. This step ensures the project is completed on time and within budget, and that the facade meets the intended design standards.
- Material Selection and Procurement: This crucial service includes research, evaluation, and sourcing of appropriate materials for the facade. This involves understanding the properties of various materials, their suitability for the building’s environment, and cost-effectiveness. The chosen materials directly impact the building’s durability, aesthetic appeal, and energy efficiency.
Key Skills and Expertise
Effective facade design requires a blend of artistic vision and technical proficiency. A successful facade designer possesses a unique combination of skills.
- Architectural Design Principles: A strong understanding of architectural principles is essential to create facades that complement the overall building design and the surrounding environment.
- Structural Engineering Knowledge: A crucial aspect of facade design is integrating the facade with the building’s structural system. This necessitates an understanding of structural load calculations and considerations for the structural integrity of the facade.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Adherence to building codes and regulations is paramount. Facade designs must comply with safety standards, accessibility guidelines, and local regulations.
- Material Knowledge: An in-depth understanding of various facade materials, their properties, and performance characteristics is essential. This knowledge allows designers to select appropriate materials that meet the project’s requirements and budget.
Successful Facade Design Projects
Several notable facade design projects showcase the complexity and innovation within this field. Each project presents unique challenges that require tailored solutions.
- The Modern Museum Facade: This project involved designing a contemporary facade that maximized natural light while maintaining structural integrity. The solution incorporated a system of glass panels that allowed for natural light penetration while providing thermal insulation and security.
- The Historic Building Renovation: This project presented the challenge of preserving the historic character of the building while updating the facade to meet modern building codes and energy efficiency standards. The solution involved meticulously researching and replicating historic materials and construction techniques while implementing modern sustainable elements.
Comparison of Facade Design Firms
| Firm | Specialization | Client Testimonials |
|---|---|---|
| A-Facade Solutions | Sustainable facades, high-rise buildings | “Excellent communication and attention to detail.” |
| B-Design Architects | Historic preservation, mixed-use projects | “Thorough understanding of building codes and regulations.” |
| C-Contemporary Facades | Contemporary designs, complex geometry | “Innovative approach to facade design.” |
Integration with Building Systems
Facade design must integrate seamlessly with the building’s structural and mechanical systems. Careful consideration of these interconnected systems ensures optimal performance and longevity.
- Structural Integration: The facade must be designed to withstand the structural loads imposed by the building, including wind loads and snow loads. This requires close collaboration with structural engineers.
- Mechanical Integration: The facade should be designed to optimize energy efficiency, managing heat transfer and daylighting. This may involve integrating solar shading devices or specialized insulation.
Client Needs and Project Requirements
Clients seeking facade design services often prioritize aesthetic appeal, durability, and energy efficiency. They typically expect a design that complements the existing building architecture and enhances its overall visual impact. Beyond aesthetics, functional considerations like weather resistance, safety, and ease of maintenance are also crucial.
A successful facade design project hinges on a deep understanding of client needs and the specific project requirements. This involves meticulous consideration of factors influencing the design process. Understanding these aspects is vital for creating a facade that meets the client’s expectations and aligns with the project’s objectives.
Common Client Needs and Expectations
Clients frequently seek facades that are not only visually appealing but also perform well in their intended environment. This involves considering factors like material selection, structural integrity, and the building’s long-term maintenance needs. They anticipate a design solution that enhances the building’s value, protects it from the elements, and improves its overall performance. A key expectation is that the design team will communicate the process and provide regular updates.
Factors Influencing Facade Design Decisions
Several factors significantly impact facade design decisions. Budgetary constraints, for example, play a major role in material choices and overall design complexity. The building’s location, with its unique climate and environmental conditions, influences the selection of materials and design features that ensure the facade withstands these conditions. Building codes and regulations often dictate the minimum standards for safety, structural integrity, and accessibility.
Importance of Clear Communication
Effective communication between clients and design professionals is paramount. Clear and consistent communication fosters a shared understanding of the project goals and expectations. This includes regular meetings, detailed design presentations, and open dialogue about design choices. A collaborative approach, where both parties actively participate and provide feedback, is crucial for a successful outcome.
Stages of a Facade Design Project
| Stage | Timeline | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Consultation and Project Definition | 1-2 weeks | Project brief, preliminary sketches, cost estimates, site analysis |
| Design Development | 2-4 weeks | Detailed drawings, 3D models, material specifications, cost breakdown |
| Permitting and Approvals | 2-6 weeks | Submitted plans, permits, and approvals |
| Construction Documents and Tendering | 2-4 weeks | Detailed construction drawings, specifications, and tender documents |
| Construction and Installation | Variable, depending on project scale | Completed facade installation, inspections, and handover |
The table above articulates the typical stages of a facade design project. The timelines are approximate and can vary depending on the complexity of the project, the availability of resources, and potential delays.
Role of Building Codes and Regulations
Building codes and regulations play a critical role in shaping facade design solutions. These regulations address safety, structural integrity, accessibility, and energy efficiency. For example, fire resistance requirements might influence the choice of materials or the design of ventilation systems. Compliance with these regulations is essential for the safety and long-term performance of the building.
“Adherence to building codes ensures the safety and structural integrity of the building.”
Codes vary regionally, necessitating a thorough understanding of local regulations.
Outcome Summary: Facade Design Services

In conclusion, facade design services go beyond mere aesthetics; they are fundamental to a building’s performance, sustainability, and overall success. From the initial concept to the final construction, careful consideration of design choices, materials, and professional expertise is key. By understanding the factors influencing design decisions and the crucial role of communication between clients and professionals, you can ensure a project that not only meets but exceeds expectations. This comprehensive guide has provided a foundation for making informed choices and maximizing the potential of facade design.





